U.S. Department of Transportation
Federal Highway Administration
1200 New Jersey Avenue, SE
Washington, DC 20590
202-366-4000
Access management refers to the design, application, and control of entry and exit points along a roadway. This includes intersections with other roads and driveways that serve adjacent properties. Thoughtful access management along a corridor can simultaneously enhance safety for all modes, facilitate walking and biking, and reduce trip delay and congestion.
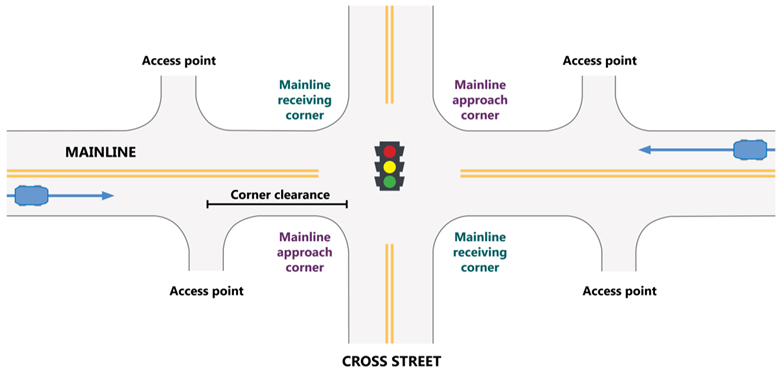
Schematic of an intersection and adjacent access points. Source: FHWA
Every intersection, from a signalized intersection to an unpaved driveway, has the potential for conflicts between vehicles, pedestrians, and bicyclists. The number and types of conflict points—locations where the travel paths of two users intersect—influence the safety performance of the intersection or driveway. FHWA developed corridor-level crash prediction models to estimate and analyze the safety effects of selected access management techniques for different area types, land uses, roadway variables, and traffic volumes.1
The following access management strategies can be used individually or in combination with one another:
Successful corridor access management involves balancing overall safety and mobility for all users along with the needs of adjacent land uses.
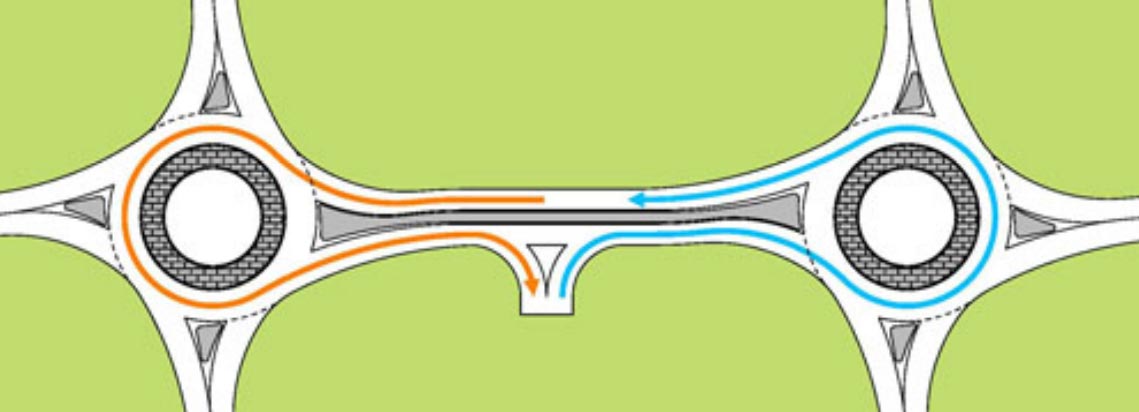

Tandem roundabouts with a continuous raised median eliminates left-turn and across-roadway conflicts. Source: FHWA
Sources
1. Gross et al. Safety Evaluation of Access Management Policies and Techniques. FHWA-HRT-14-057, (2018).
2. Le et al. Safety Evaluation of Corner Clearance at Signalized Intersections. FHWA-HRT-17-084, (2018).
3. Harwood et al. Prediction of the Expected Safety Performance of Rural Two-Lane Highways. FHWA-RD-99-207, (2000).
4. Elvik, R. and Vaa, T., Handbook of Road Safety Measures. Oxford, United Kingdom, Elsevier, (2004).
Filter countermeasures by focus area, crash type, problem identified, and area type.
