U.S. Department of Transportation
Federal Highway Administration
1200 New Jersey Avenue, SE
Washington, DC 20590
202-366-4000
While most transportation agencies have established traditional safety review procedures, a road safety audit (RSA) or assessment is unique. RSAs are performed by a multidisciplinary team independent of the project. RSAs consider all road users, account for human factors and road user capabilities, are documented in a formal report, and require a formal response from the road owner. (See the eight steps for conducting an RSA below.)
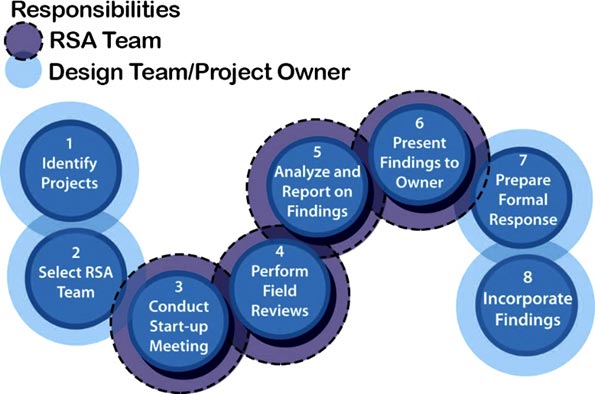
Source: FHWA
RSAs provide the following benefits:
RSAs can be performed in any phase of project development, from planning through construction. Agencies may focus RSAs specifically on motorized vehicles, pedestrians, bicyclists, motorcyclists, or a combination of these roadway users. Agencies are encouraged to conduct an RSA at the earliest stage possible, as all roadway design options and alternatives are being explored.
Sources
1. Road Safety Audits: An Evaluation of RSA Programs and Projects, FHWA-SA-12-037; and FHWA Road Safety Audit Guidelines, FHWA-SA-06-06.
Filter countermeasures by focus area, crash type, problem identified, and area type.
